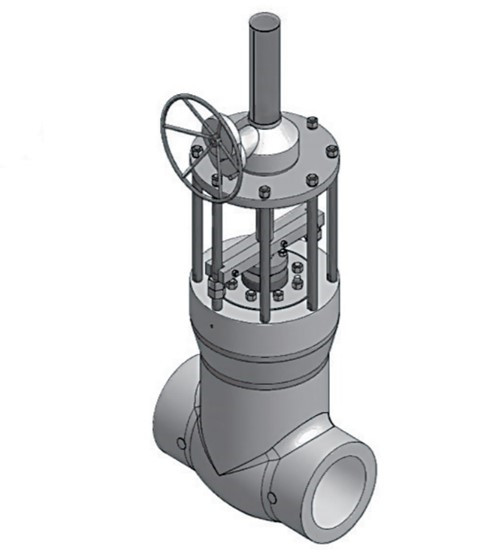
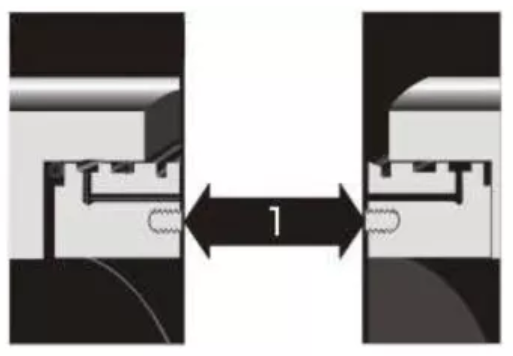
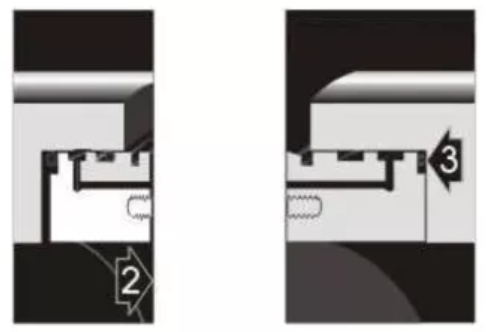
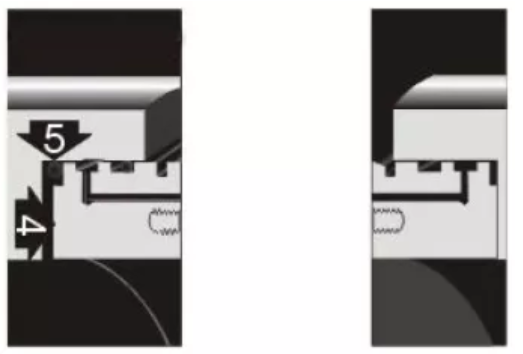
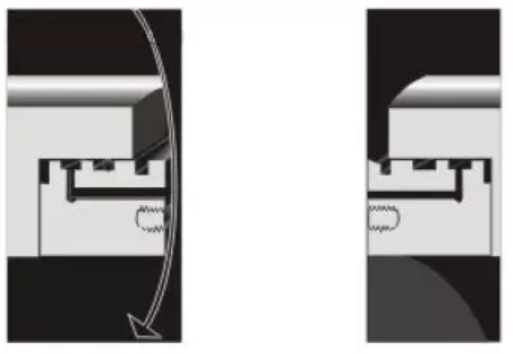
Comparison Slab Gate Valve VS Wedge Gate Valve
Slab gate valve and wedge gate valves are all designed for use in power, oil and gas industry applications. They are the main and commonly used types of gate valves. They have the similar structure form the appearance, when fully open, they do not have a bore through the gate itself and the gate retracts into the valve body, saves height space that is necessary for slab and expanding gate valves. Today here we will introduce the difference between slab and wedge type gate valve.
Slab Gate Valve
Slab gate valves are comprised of a single gate unit which raises and lowers between two seat rings. Due to the fact that the gate slides between the seats, slab gate valves are suitable for the medium with suspended particles. The sealing surface of slab gate valves is virtually self-positioned and is not damaged by the thermal deformation of the body. Even if the valve is closed in a cold state, the hot elongation of the stem does not overload the sealing surface, and slab gate valves without diversion holes do not require high precision in the closing position of the gate. When the valve is fully open, the bore through is smooth and linear, the flow resistance coefficient is minimal, piggable and no pressure loss.
Slab gate valves also have some disadvantages: when the medium pressure is low, the metal sealing surface may not seal completely, instead, when the medium pressure is too high, the highly-frequency opening and closing may make the sealing surface wear too much when there is no medium or lubrication. Another drawback is that a circular gate that moves horizontally on a circular channel controls flow effectively only when it is at 50% of the valve’s closed position.
Slab gate valves applications
Single or double-disc slab gate valves are suitable for oil and gas pipelines with DN50-DN300, class150-900 / PN1.0-16.0 Mpa, operating temperature -29 ~ 121℃. In the case of pipeline with piggable design, use a rising stem gate valve with a diversion hole. The slab gate valve with a diversion hole with a dark rod floating seat is suitable for oil and gas recovery wellhead device. The product oil pipeline and storage equipment shall use a single gate or double gate flat gate valves without diversion holes.
Wedge type gate valves
Wedge gate valves are comprised of a tapered gate that is metal-to-metal sealing. Compared with a slab gate valve, wedge gate valves are not piggable because of the void that is left in the bottom of the valve body when the valve is open. The wedge design increases the auxiliary sealing load, enabling metal sealed wedge valves to seal at both high and low medium pressures. However, wedge gate valves with metal seals are often unable to achieve the inlet seal due to the specific pressure of the inlet seal caused by the wedge action. Wedge gate valves have a certain Angle, generally, 3 degrees or 5 degrees, resulting in accumulated material in the lower groove of the valve, the medium with the particulate matter may damage the sealed seat, make loose closure.
Wedge gate valve application
Wedge gate valves are generally used where has no strict requirements of the size of the valve and harsh occasion. Such as high temperature and high pressure working medium, the requirements to ensure the closure of the long – term sealing conditions. Normally, for the environment with reliable sealed performance, high pressure, high-pressure cut-off (differential pressure) and low pressure by the (small) differential pressure, low noise, have spirit point and evaporation phenomena, the high temperature, low temperature, cryogenic medium, it is recommended to use wedge gate valve such as the electric power industry, oil refining, petrochemical, offshore oil, tap water and wastewater treatment engineering of urban construction, chemical industry, etc.