How many types of globe valve do you know?
The globe valve is designed with a stem that moves up and down to allow the medium flow one-way movement and make the sealing surface of the valve disc and seat tightly fit to prevent medium flow. It’s characterized saving elbow and operate conveniently and can be installed in the bent part of the pipeline system. There are various types of globe valve and designs, each with their own pros and cons. In this blog, we will introduce the classification of globe valves in details.
The flow direction of globe valve
- Tee shape/Split body globe valve
The design making inlet and outlet channels of the valve are 180° in the same direction and has the lowest coefficient of flow and highest pressure drop. Tee/Split type globe valve can be used in severe throttling services such as in bypass line around a control valve. - Y pattern globe valve
Its disk and seat or the seat sealing an inlet/outlet passage present a certain angle, usually 45 or 90 degrees to the pipe axis. Its fluid hardly changes flow direction and has the least flow resistance in the globe valve types, suitable for coke and solid particles pipeline.
3. Angle pattern globe valves
Its flow inlet and outlet are not in the same direction with a 90° angle, which produces certain pressure drop. The angle globe valve is characterized by its convenience and without the use of an elbow and one extra weld.
Stem and disc of globe valves
- Outside screw stem stop valve
The stem thread is outside of the body without connection with the medium to avoid the corrosion, easy to lubricate and operate. - Inside screw stem stop valve
The inner valve stem thread contact directly with the medium, easy to be corrosion and cannot be lubricated, usually used in the pipeline with the small nominal diameter and the medium working temperature is not high. - Plug disc globe valve
Plug valve is also known as the plunger globe valve. With a radial sealing structure design, by the polished plunger on the two elastic sealing ring through the body and bonnet connection bolt applied on the bonnet load around the elastic sealing ring to achieve the sealing of the valve.
4. Needle globe valve
Needle globe valve is a kind of small diameter instrument valve, which plays the role of opening and closing and flows control in instrument measuring pipeline system.
5. Bellows globe valve
Formed stainless steel bellows design offers reliable sealing performance, suitable for flammable, explosive, toxic and harmful media occasions, can effectively prevent leakage.
Applications of globe valves
- PTFE-Lined globe valve
PTFE Lining globe valve is the valve that molding(or inset) Polytetrafluoroethylene resin in the inner wall of the metal valve pressure piece (the same method applies to all kinds of pressure vessels and pipe accessories lining) or the outer surface of the valve inner piece to resist the strong corrosive medium of the valve. PTFE lined globe valve is applicable to Aqua regia, sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and various organic acids, strong acids, strong oxidants at various concentrations of -50 ~ 150℃, as well as strong alkali organic solvent and other corrosive gases and liquid medium in the pipeline. - Cryogenic globe valve
Cryogenic globe valves usually refer to valves operating below -110℃. It is widely used in liquefied natural gas, petroleum and other low-temperature industries. At present, the globe valve with an applicable temperature of -196℃ can be manufactured, which uses liquid nitrogen for low-temperature pretreatment to completely avoid sealing deformation and leakage.
PERFECT manufacture and supply globe valves according to ANSI and API standards, the valve disc and seat sealing surface are made of stellite cobalt carbide surfacing that offering various advantages like reliable sealing, high hardness, wear resistance, high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, abrasion resistance and long service life. We design each valve according to the flow parameters presented. Contact our sales representative for details.


 In the United States institutions system, there are several standards can be used to specify the industrial valve like ASME standard ( American Society of Mechanical Engineers), API standard (American Petroleum Institute), ANSI standard (American National Standards Institute), MSS SP standard (Manufacturers Standardization Society of the Valve and Fittings Industry). Each of them has specific specifications for valves and complements each other, here we collect a series of commonly used valve API standards for general industrial valves.
In the United States institutions system, there are several standards can be used to specify the industrial valve like ASME standard ( American Society of Mechanical Engineers), API standard (American Petroleum Institute), ANSI standard (American National Standards Institute), MSS SP standard (Manufacturers Standardization Society of the Valve and Fittings Industry). Each of them has specific specifications for valves and complements each other, here we collect a series of commonly used valve API standards for general industrial valves.


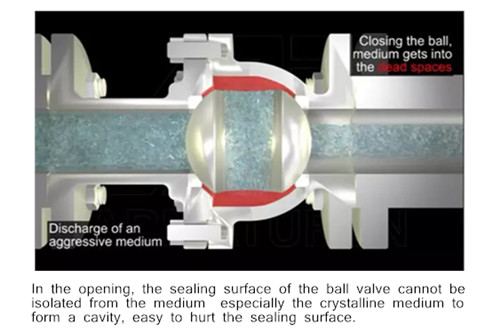
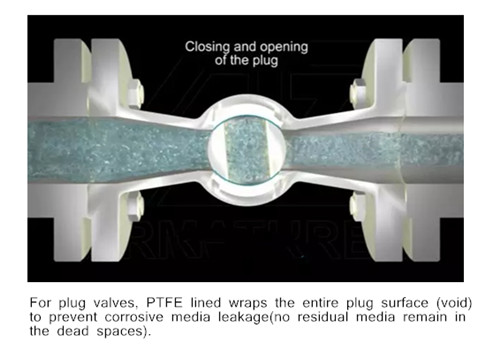 between the plug and the gap between the body. Plug valve is simple and often economical because it usually does not have bonnets, but the handle exposed outside at the end instead.
between the plug and the gap between the body. Plug valve is simple and often economical because it usually does not have bonnets, but the handle exposed outside at the end instead.
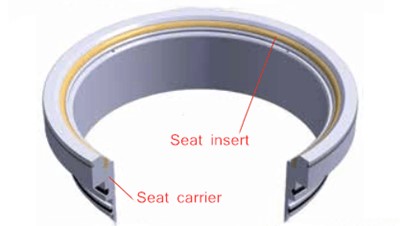 When choosing an industrial valve, you will face numerous choices. Available materials, proper size, and design (1, 2, or 3 pieces, end connections, etc.) are the key factors to decide which type of valve to use. Equally important is the type of valve seats which directly determines the leakage class of the valve. Before you choose the right valve seats, you must know the following question: Is the medium corrosive? Contains abrasive particles? For high temperature or high pressure? Once you know these things, you will make the right choice. Therefore, the first step to fully understand your craft condition: choose a suitable valve seat.
When choosing an industrial valve, you will face numerous choices. Available materials, proper size, and design (1, 2, or 3 pieces, end connections, etc.) are the key factors to decide which type of valve to use. Equally important is the type of valve seats which directly determines the leakage class of the valve. Before you choose the right valve seats, you must know the following question: Is the medium corrosive? Contains abrasive particles? For high temperature or high pressure? Once you know these things, you will make the right choice. Therefore, the first step to fully understand your craft condition: choose a suitable valve seat.