The extraction check valve for high pressure turbine
In the last article, we introduced the ventilator valve, blowdown valve and reverse flow valve for turbine system, here today we will continue talking about the extraction check valve for high-pressure turbine When the valve opens, the cylinder takes steam, the flowing medium pushes the valve plate to open the valve, the greater the medium flow, the greater the spool opening; When the valve is closed, the solenoid valve quickly loses power and expunges the air in the cylinder. In addition to the dead weight of the valve plate and the auxiliary closing force of the cylinder, the valve is quickly closed.
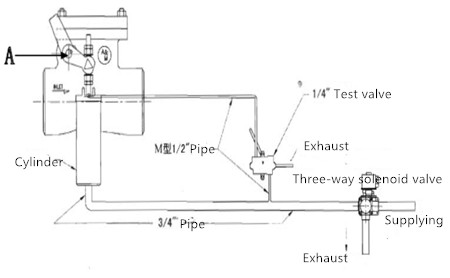
The high-pressure turbine steam-exhaust check valve is installed in the horizontal pipeline of the steam turbine reheating and cooling section to prevent water and steam from pouring back into the high-pressure cylinder and affecting the safety of the steam turbine. Specially designed for steam turbine exhaust protection, their fast and tight closure ensures that water or steam can be quickly isolated from the steam turbine while the generator is tripped or the main steam valve is closed. The valve will close automatically when the high water level of heating equipment in the turbine tripping or all levels of extraction steam pipelines. As a protective device, the extraction check valve must be reliable.
High-pressure cylinder exhaust steam pressure: Reheater inlet pressure
High-pressure cylinder exhaust temperature: ≤420℃
Extraction pressure of each section: vacuum ~10MPa
Extraction temperature of each section: 200~510 ℃
Valve pressure range:
ASME B16.34 1996 –150 Class
ASME B16.34 1996 – 300 Class
ASME B16.34 1996 –400 Class
ASME B16.34 1996 –600 Class
Valve body: Cast steel
ASTM A216-WCB
ASTM A217-WC6/WC9(1# /3#extraction)
Actuator:
For large units, the steam extraction reverse check valve is mainly driven by pneumatic, while it is hydraulic for small and medium-sized units.
The type of extraction check valve
According to the opening /closure parts:
- Self-weight closing. Self-weight close (close): Check valve closed by the self-weight or counterweight of the trim or depending pressure of medium and counterweight of trim to keep it in the open position of the valve.
- Power-assisted closing. The actuator provides a pulse point action to make the spool overcome the initial inertia caused by being in the closed position for a long time or external causes and complete the rest travel by itself to close the valve.
- Power closing. During the closing process, the actuator always provides power to complete all the travel of the spool and close the valve.
According to its structure:
- Steam extraction reverse check valve without a hammer
IBS internal balancing shaft steam extraction reverse check valve without a hammer. Internal balance refers to the internal balance of the dead weight of the spool. The spool is supported by the shaft and rotates freely around the shaft. They are not connected directly but are connected with the piston of the side working cylinder. The actual opening inside the valve cannot be confirmed.
- Steam extraction check valve with a heavy hammer
A large diameter valve offers heavy trim, then a heavy hammer can be used in the extraction steam check valve, hammer can offset part of the trim weight (about half of the spool). The valve trim is directly connected to the shaft, and the actual opening inside can be seen from the angle changes of the exterior tumbler. If the inside is not fully open, it can be observed from the outside. The valve is a free swing, gravity closed check valve, when the inlet pressure is higher than the outlet valve trim open, while the valve closed on the contrary.



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!